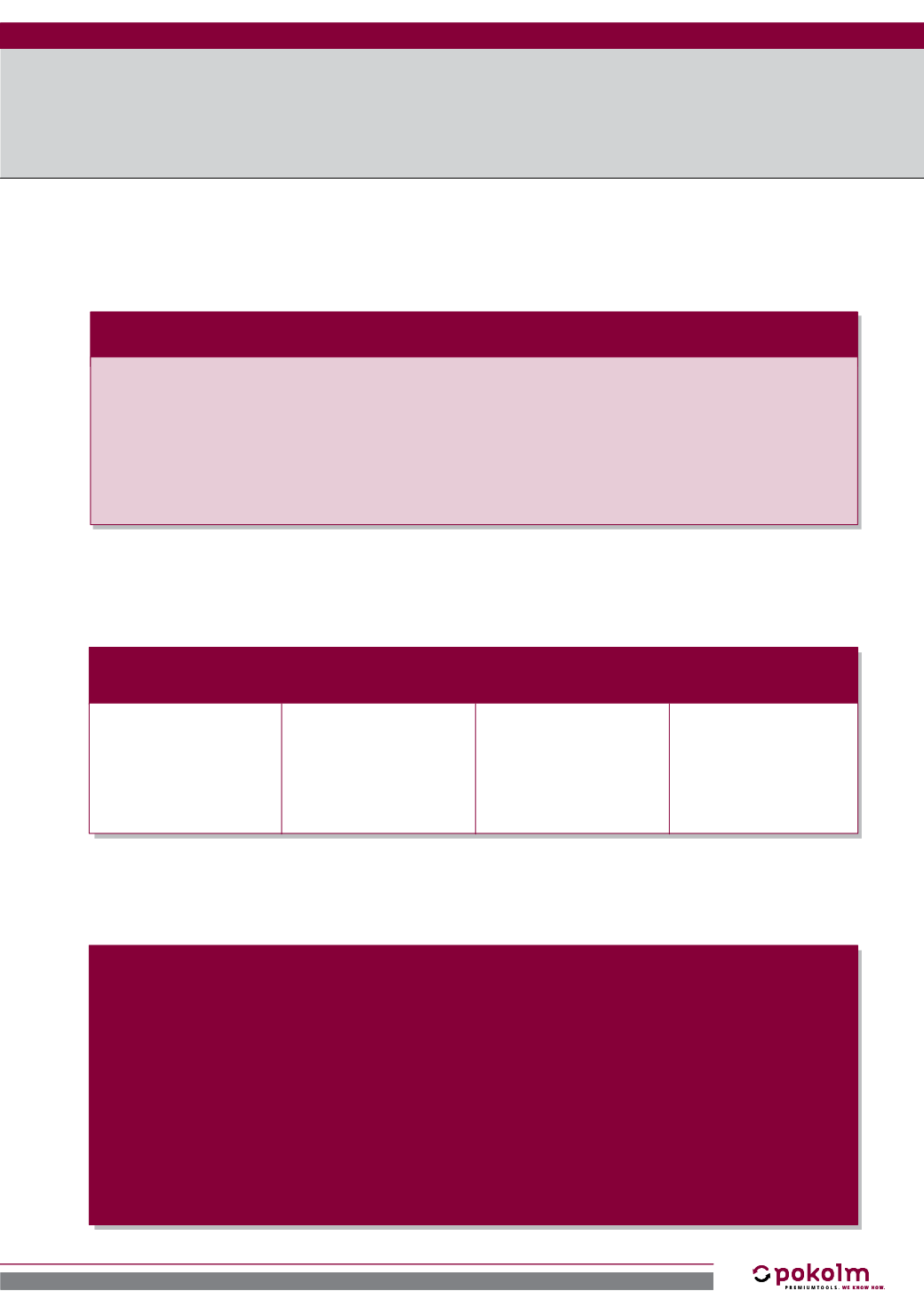
e=
U
–
m
ω
=
2·
π
·n
–––––
60
G=e·
ω
=
U·
π
·n
–––––
m·30
m
r
=
e·m
––––
r
CALCULATIONS AND DEFINITIONS
G 0,4
G 1
G 2,5
G 6,3
G 16
G 40
e.g. microfinishing machines
e.g. low-power motors, driving gears for grinding machines
e.g. cutting tools, small arbors and adapters, electrical motors, turbines
e.g. cutting tools, arbors and adapters, machine tool parts
e.g. big arbors, cardan shafts, drive shafts
e.g. universal shafts, automotive wheels, crank gear drives
Balancing grade classifications and typical applications:
Formulas:
Calculation of remaining
balance error in [gmm/kg]
Calculation of radian
frequency in [1/s]
Calculation of balancing
grade levels in [mm/s]
Calculation of
compensation mass
Definitions and dimensions:
= balancing grade level in [mm/s]
= balance error [m · e] in [gmm]
= remaining balance error in [gmm] or
eccentricity of center in [
µ
m]
= rotor weight in [g]
= frequency (n/60) in [1/s]
= remaining balance error in [mm]
= rpm
= remaining balance error [g]
= radian frequency (2 •
π
• f) in [1/s]
= centrifugal force (U • ) in [N]
G
U
e
m
f
r
n
m
r
ω
F
7
Calculations and definitions


